Lab 08: Spatial Analysis Buffering and Overlay
1 Introduction
In this lab, we will explore spatial analysis techniques using buffering and overlay operations in ArcGIS. These techniques are fundamental in geographic information systems (GIS) and are often used to determine spatial relationships between various features.
2 Objectives
- Apply the concepts of buffering and overlay in GIS.
- Create maps demonstrating buffer zones and suitable areas for specific land use.
- Perform spatial analysis to identify potential campgrounds based on proximity to lakes and roads.
3 Tasks
3.1 1. Create Buffer Zones
Using the provided data (lakes.shp, roads.shp), generate buffer zones around lakes and roads. Apply variable distance buffers for lakes based on their size and fixed distance buffers for roads.
3.2 2. Perform Overlay Analysis
Overlay the buffer zones to identify areas that meet both the criteria for being near a lake and a road. Use the union operation to combine these layers and identify suitable areas for potential campgrounds.
3.3 3. Analyze Suitable Areas
Determine the size of the suitable areas identified in the overlay analysis. Calculate the area in hectares and create maps that display these areas.
4 Results
4.1 Hugo Minnesota Lakes and Roads - Buffer Zones
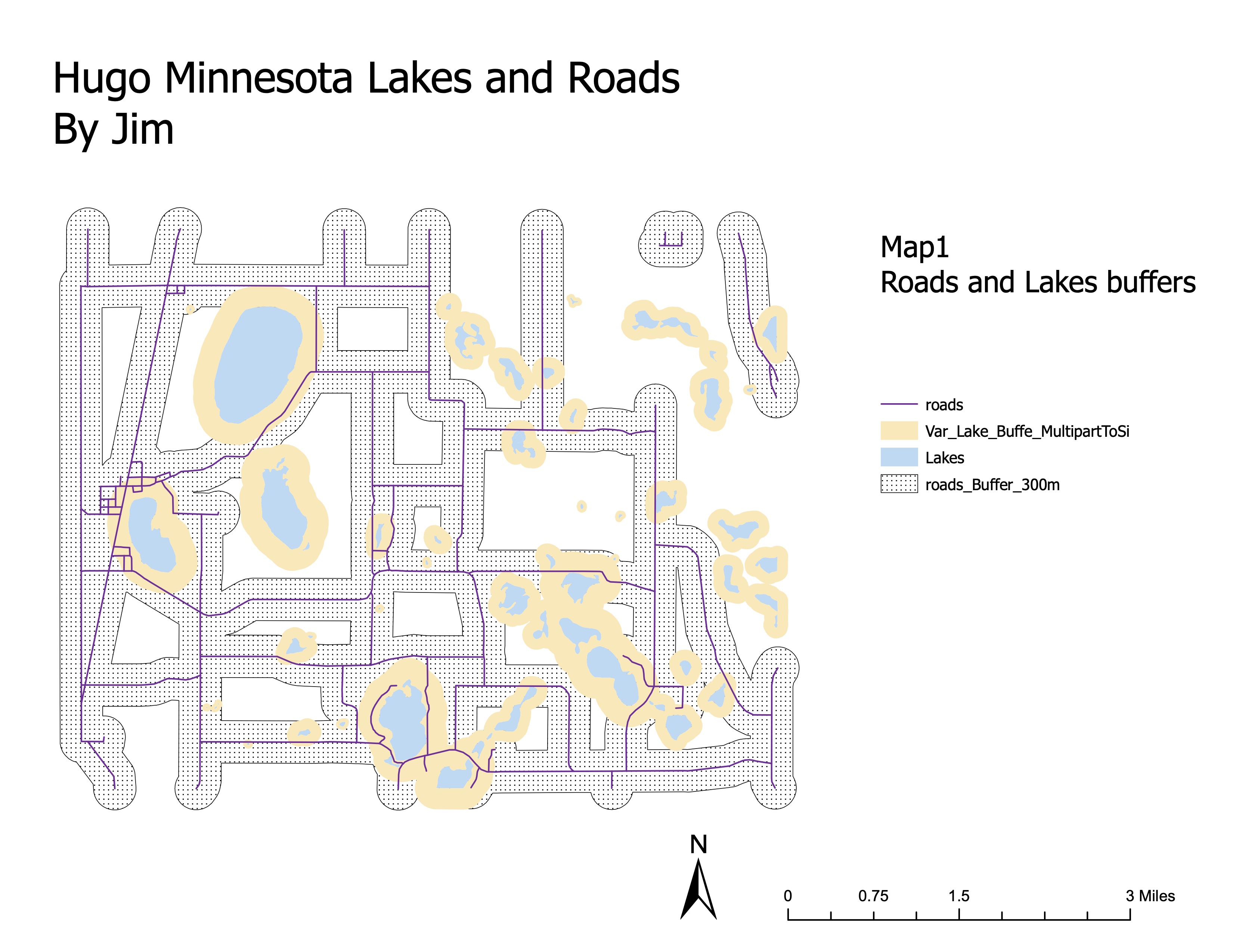
4.2 Hugo Minnesota Lakes and Roads - Overlay Analysis
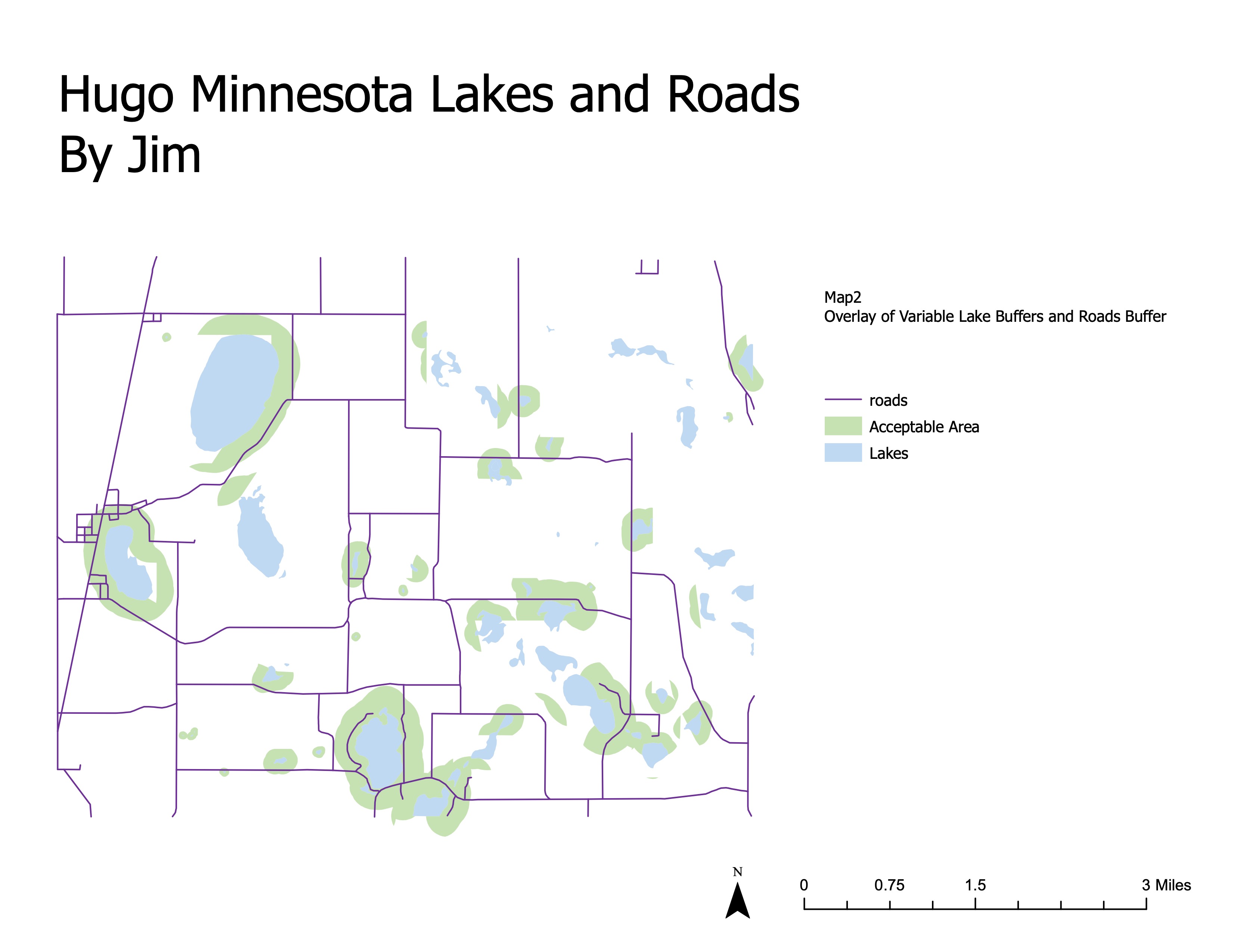
4.3 Hugo Minnesota Lakes and Roads - Campground Locations
.jpeg)
5 Conclusion
This lab demonstrated the use of buffering and overlay operations in GIS to identify suitable areas for campgrounds. By applying these spatial analysis techniques, we can make informed decisions about land use based on proximity to key features such as lakes and roads.